
In the category of Research and Program Evaluation on the National Counselor Examination (NCE), the Counselor Preparation Comprehensive Examination (CPCE), or another counseling exam, it will be helpful for you to understand what ANOVA means. An Analysis of Variance—or ANOVA—is a concept you’ll almost certainly come across in your research class. It’s also a concept to be aware of to help you with the Research and Program Evaluation questions on your counseling exams.
What is an ANOVA? An analysis of variance—more often abbreviated ANOVA—is a way to examine if more than two groups have a statistically significant difference in their mean. Meaning, when a study is complete and the data are being analyzed, an ANOVA can help determine if there is a meaningful difference between more than two groups within the study. If this is confusing, keep reading about one-way and two-way ANOVAs and it will likely start to make a bit more sense!
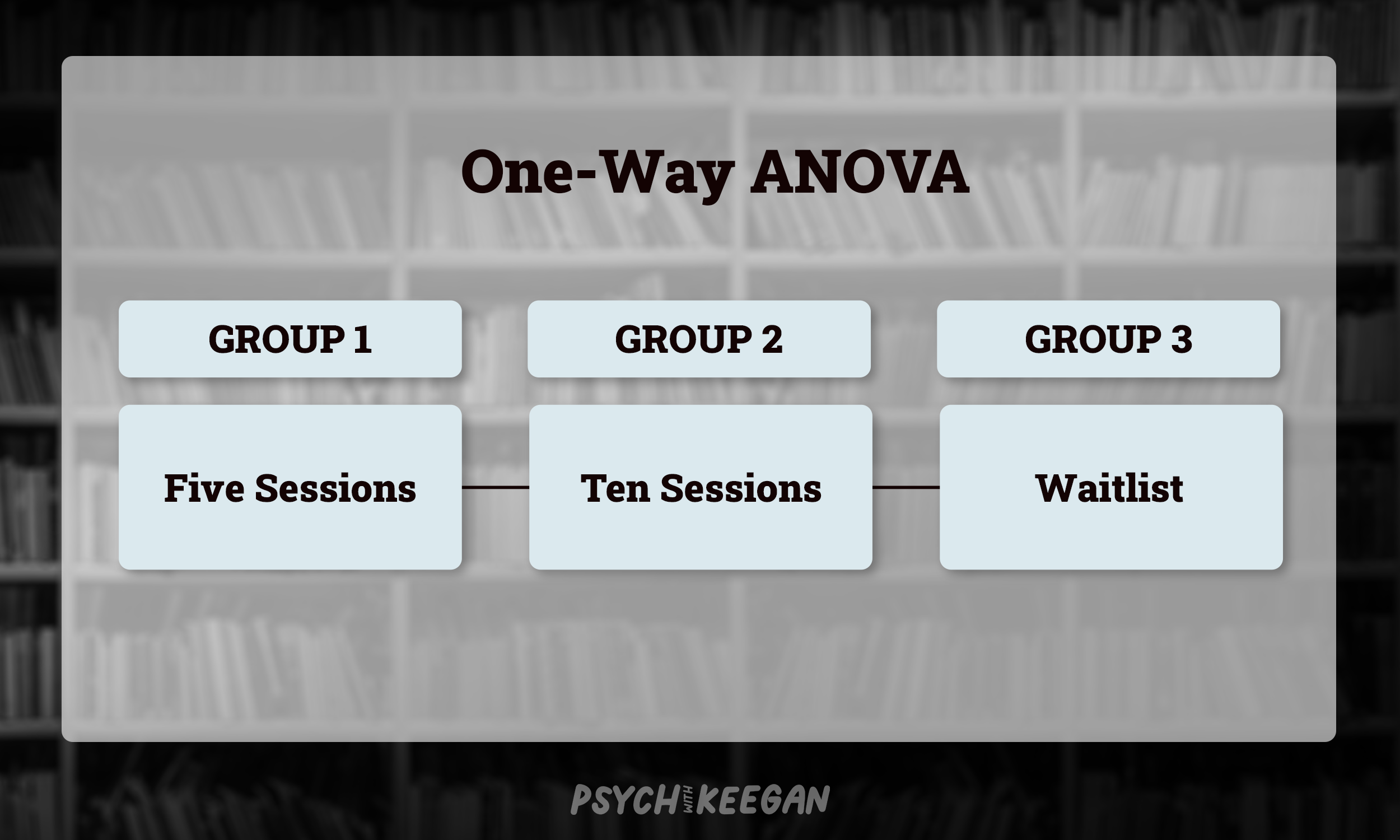
What is a One-Way ANOVA? A one-way ANOVA looks at one independent variable amongst three or more groups within a study. Let’s use an example to help understand this idea. Imagine we have three groups that are receiving therapy. Group one is completing five sessions of therapy, group two is completing 10 sessions, and group three is a waitlist group (who are not receiving therapy). In this case, the independent variable is their treatment (how much therapy they are receiving). The ANOVA is comparing this between the groups to determine the effectiveness of the groups. Since we are only looking at the amount of therapy, a one-way ANOVA would be used.
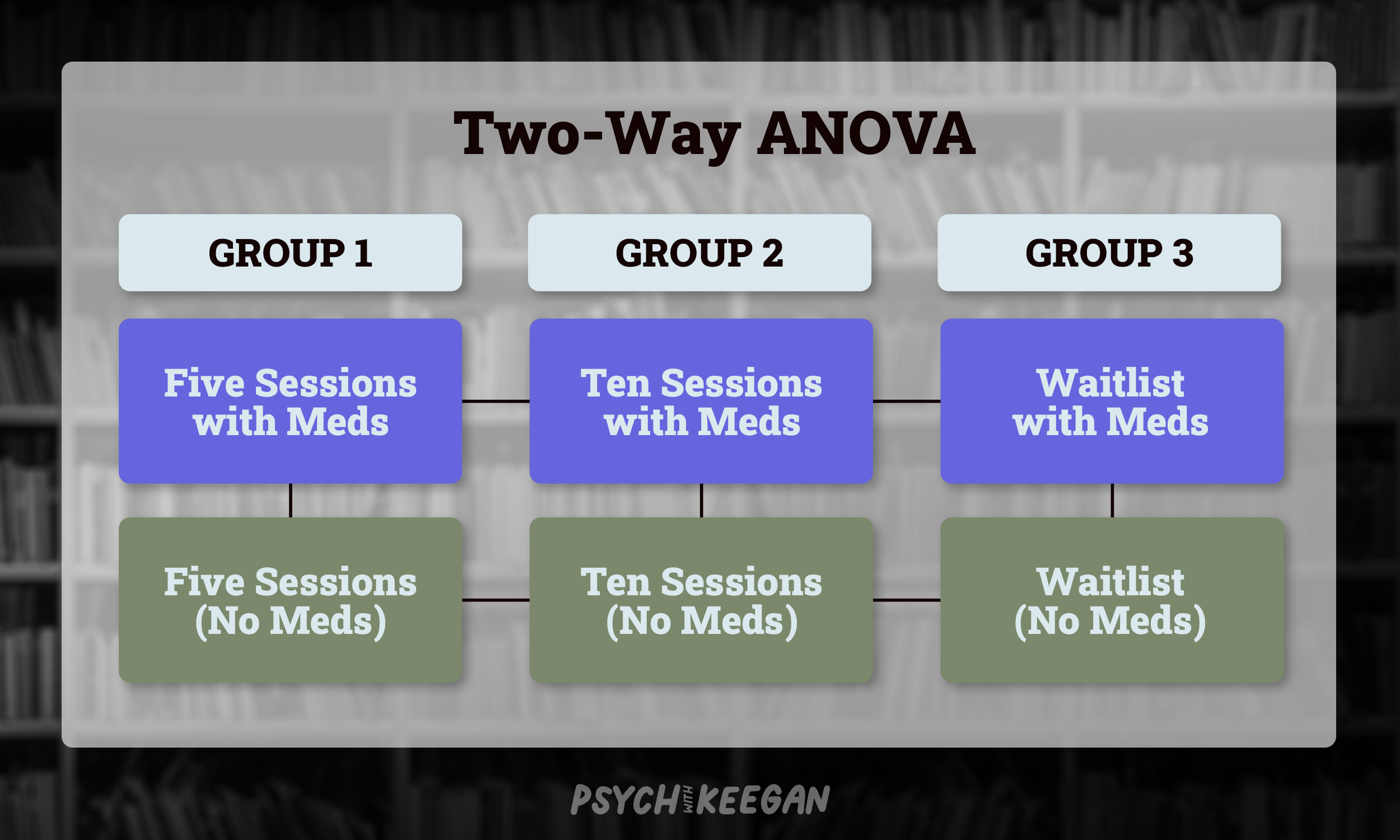
What is a Two-Way ANOVA? A one-way ANOVA tests one independent variable, meaning that a two-way ANOVA tests two independent variables. Let’s continue the example from above. If we take the three groups and give them the same treatments and also now give half of each group medication, and don’t give the other half medication, a two-way ANOVA would be used here. The two-way ANOVA is used because we need to look to see if the amount of therapy made a difference as well at whether medication (or no medication) also made a difference.
How are the results of an ANOVA determined? When you run an ANOVA, the result is an F-value or F-statistic. This result is compared with an F-table to get the critical value of F. When the F value exceeds the critical F, the null hypothesis is rejected.
What is a Null Hypothesis? To explain what a null hypothesis is, we will have to think about when you have an experiment. With an experiment, you will have at least two hypotheses. The first is the experimental hypothesis. The experimental hypothesis is what you feel might happen in the experiment or what you hypothesize the results might be. The null hypothesis is when there are no differences between the groups. Therefore, when the null hypothesis is rejected, that would mean that your experiment showed results.
What is a MANOVA? You might hear about a multivariate analysis of variance, or MANOVA. This is when there is more than one dependent variable. The dependent variable being the data you are measuring in an experiment.
What is an ANCOVA? If you hear about an ANCOVA, this is an analysis of covariance. An ANCOVA controls for the impact that one or more covariates have on the dependent variable. As a reminder, a covariate is an extraneous or unstudied variable.


If you or someone you know are needing immediate mental health assistance, please call or text 988, contact a local emergency telephone number, or go to the nearest emergency room.
By interacting with this website and channel, this does not constitute a therapist/client relationship. This content is intended for the purposes of entertainment and mental health education.
View additional disclaimers and notices on our Disclaimers page.